Structural Designs:
Beyond the basic types, FIBC bags also differ in structural design and features:
- U-Panel Bulk Bags: This type of bulk bag consists of a three-part structure: a complete piece of fabric extending from the bottom of the bag to both sides, forming a "U" shape, and two additional pieces of fabric sewn on either side of the "U"-shaped fabric , forming two additional panels. This design helps maintain the square shape of the bulk bag after filling.
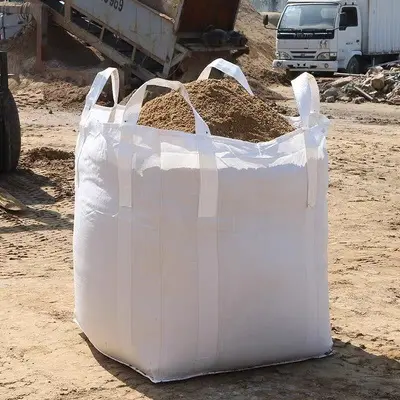
- Round Bulk Bags: Round bags are typically made from a continuous loop of fabric sewn at the top and bottom only. Bulk bags with this structure look like square bags when filled, but are not actually truly round.
- Four-Panel Bulk Bags: Four-panel bulk bags are sewn with four side panels and a bottom panel to better maintain their square shape when loaded.
- Barrier Bulk Bags: Barrier bulk bags add partitions to the interior of U-shaped, four-panel or round bulk bags. These dividers help the bag stay square after filling, improving stability and stackability. Therefore, clapboard bulk bags are called "Q bags".
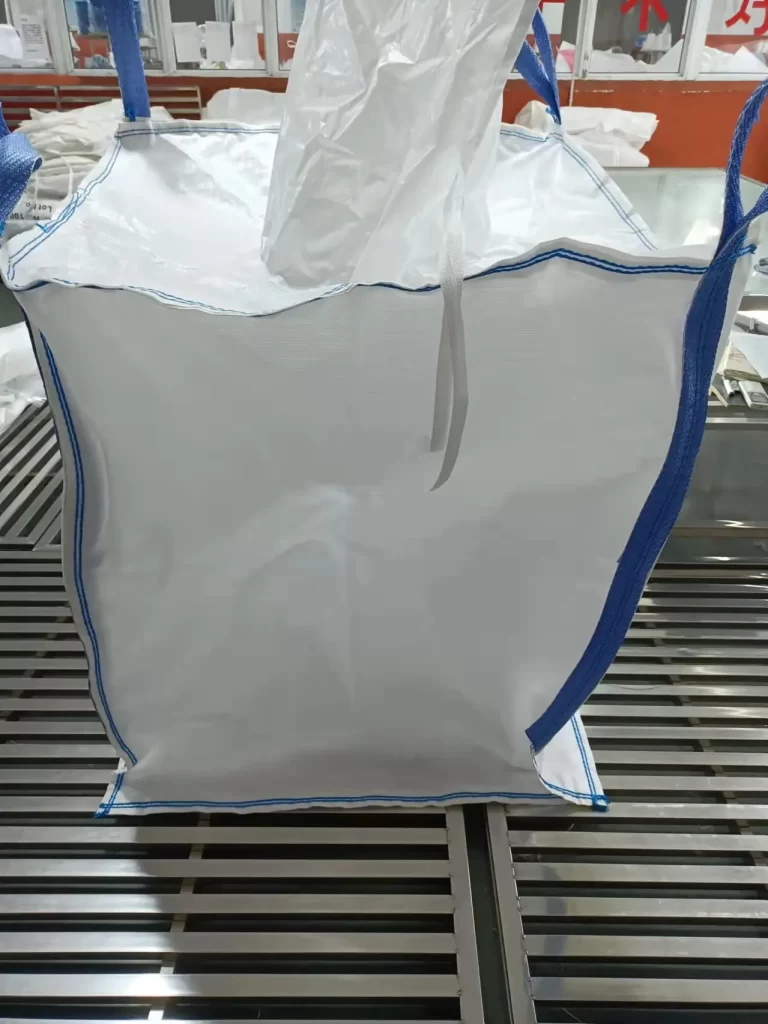
- Single-ring and double-ring bags: The hanging rings of this bulk bag are an extension of the bag fabric, that is, the bag fabric directly forms the hanging rings. This design makes the bulk bags easier to lift and relatively low cost.
In addition, FIBC bags can also be divided into coated and non-coated types according to whether they are coated or not.
Coated FIBC bags:
Advantage:
Moisture Resistant: The polypropylene film layer blocks moisture and protects interior materials from moisture damage.
Dustproof: Blocks dust and particles to keep the product clean.
Stable woven mesh: Enhances bag structure, improves load-bearing capacity and durability.
Leak-proof: Prevents leakage of powder or granular materials.
Shortcoming:
Poor breathability: Not suitable for products that need to breathe or release gas.
Higher cost: The coating process increases production costs.
Not suitable for high temperature environments: High temperatures may cause the coating to melt or crack.
Uncoated FIBC bags:
Advantage:
Good breathability: allows air circulation, suitable for products that need to breathe or release gas, such as fresh produce or chemical products.
Lower cost: no coating process, production cost is relatively low.
Suitable for high temperature environments: resistant to high temperatures and will not melt or crack due to high temperatures.
Shortcoming:
Poor moisture resistance: Not waterproof and easily damaged by moisture.
Poor dust resistance: unable to block dust and particles and may contaminate products.
Poor stability: load-bearing capacity and durability are not as good as coatings.